Comprehensive Health Check
- Home
- The Fukushima Health Management Survey
- Comprehensive Health Check
Implementation Status
Number of eligible persons, participants, and participation rates
Residents ages 15 and younger
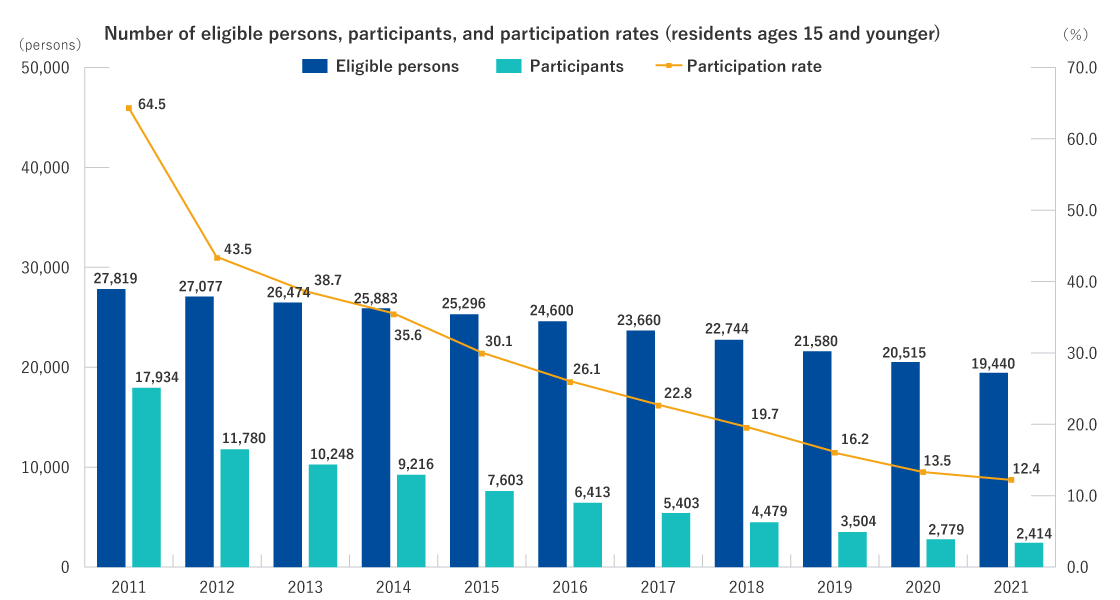
- The participation rate for ages 15 or younger in FY2022 was 9.3%, down by 3.1 points compared with a participation rate of 12.4% for FY2021.
Residents ages 16 and older
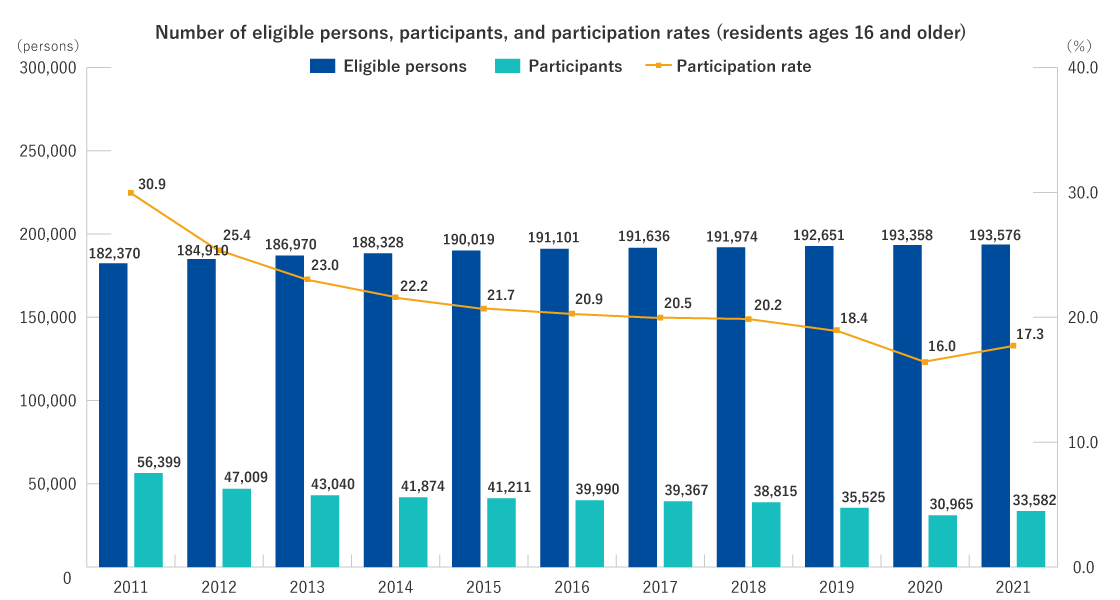
- The participation rate of those ages 16 and older was 17.7% in FY2022. Compared with the rate of 17.3% in FY2021, it was a 0.4 point increase. The main reason for this increase is thought to be that those who had refrained from receiving a Health Check due to concerns over COVID-19 infection began to participate in FY2022.
Yearly changes in major Health Check items (Age Group: 15 or younger)
Obesity
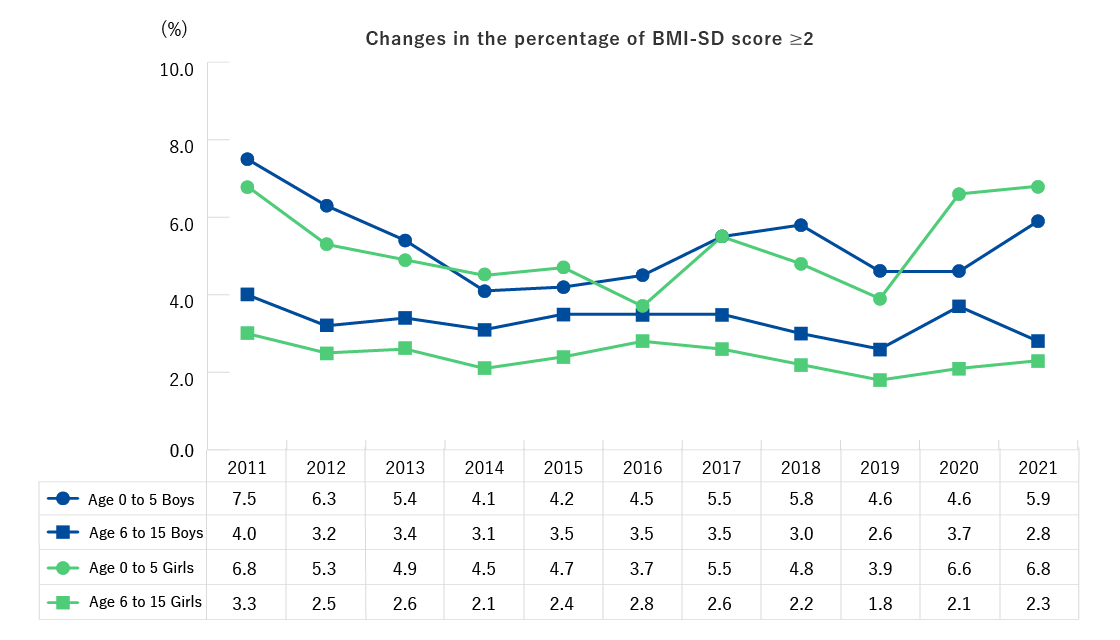
- The percentage with obesity (BMI-SD score ≥2) among boys ages 0 to 5 at the time of participation was highest in FY2011, and showed gradual decrease to FY2014, but has not shown a consistent trend thereafter.
- The percentage with obesity (BMI-SD score ≥2) among girls ages 0 to 5 at the time of participation was also highest in FY2011, and showed gradual decrease to FY2016, but has not shown a consistent trend thereafter.
- The percentage with obesity (BMI-SD score ≥2) among both boys and girls ages 6 to 15 at the time of participation was highest in FY2011, and showed gradual decline to FY2016, but has not showed a consistent trend thereafter.
* Calculated BMI Standard Deviation Score (BMI-SD Score), based on height and weight measurements, determined ≥2 as obesity.
Lipid abnormality
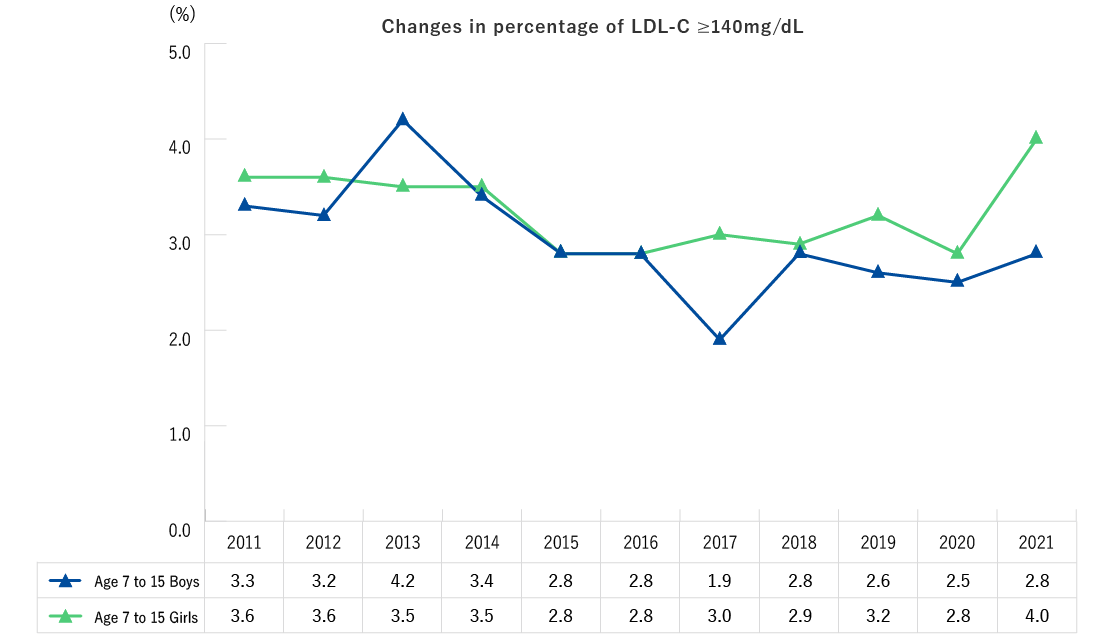
- The percentage of both boys and girls with LDL-C levels of 140 mg/dL or over showed no certain trends.
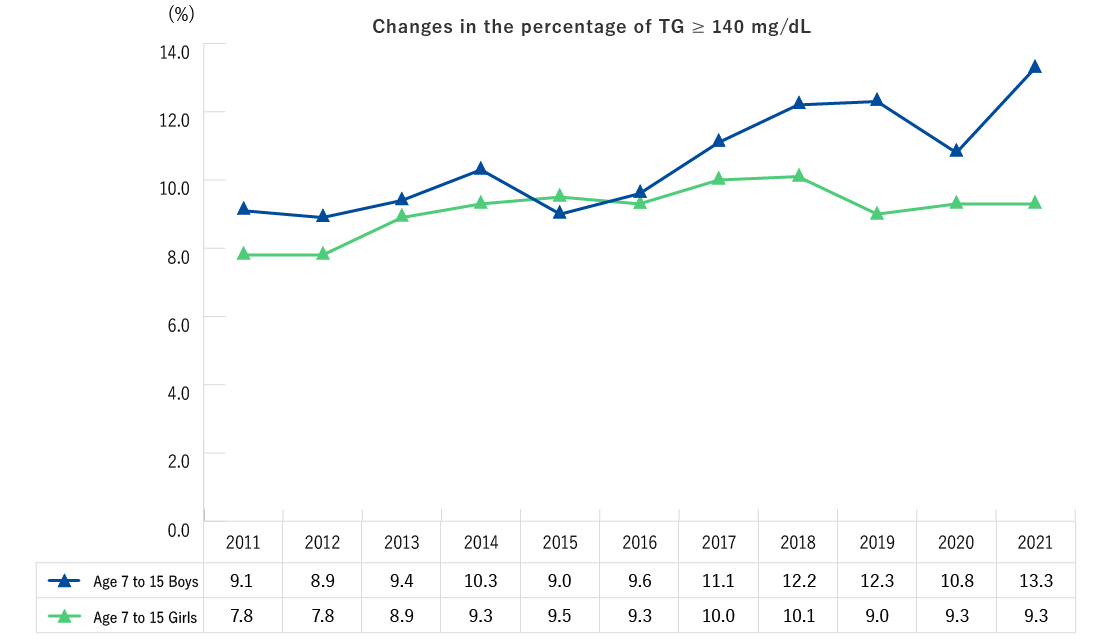
- The percentage of boys with triglyceride levels of 140 mg/dL or over showed no certain trend. For girls, there were no substantial changes.
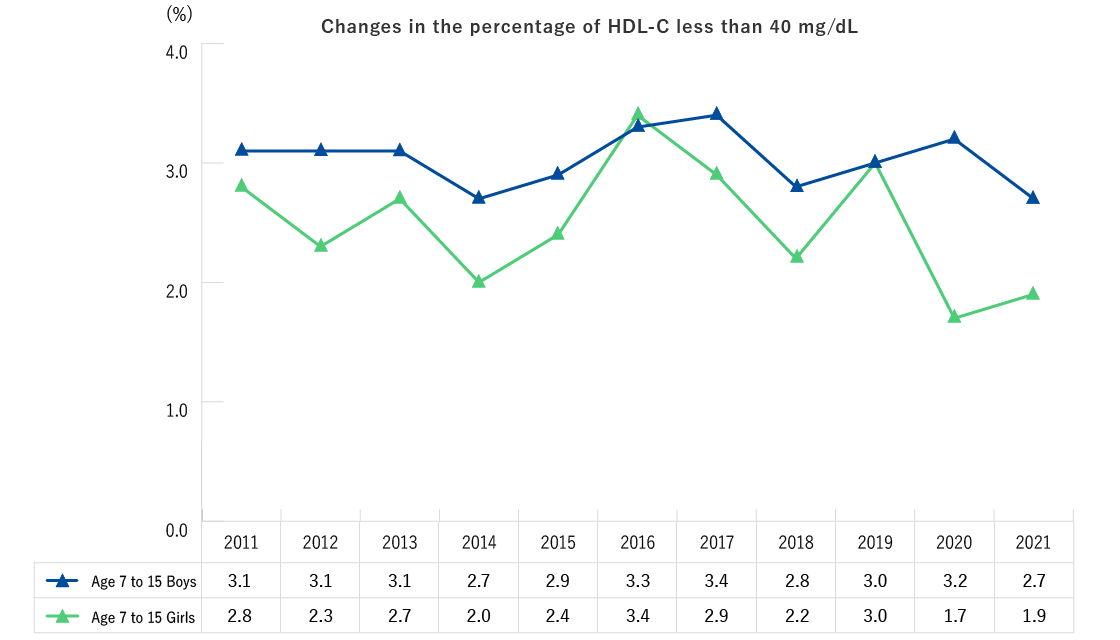
- There were no certain trends in the percentage of both boys and girls with HDL-C levels lower than 40 mg/dL.
* Lipid abnormalities were determined based on criteria of the Japan Atherosclerosis Society (JAS) Guidelines for Prevention of Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Diseases 2022.
Year-to-Year Changes in Major Results (Age groups of 16 to 39, 40 to 64 and 65 and older)
Obesity
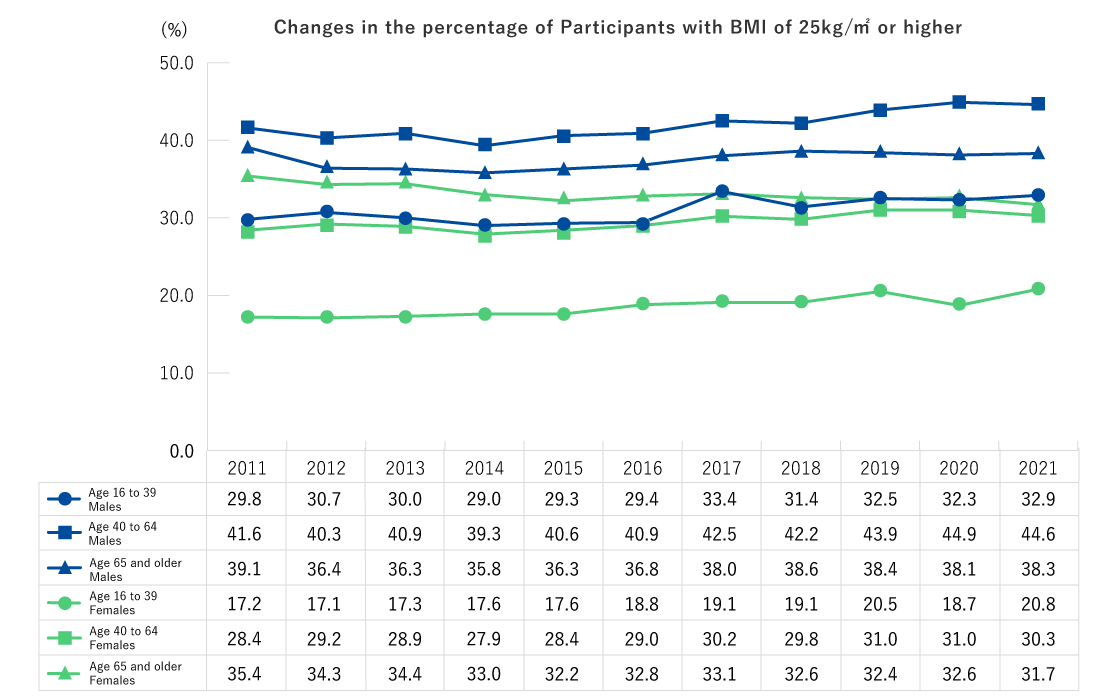
- For males, the percentage of males with a BMI of 25 kg/m2 or over increased in FY2017 for all age groups, with no substantial changes thereafter to FY2022.
- The percentage of females with a BMI of 25 kg/m2 or over showed an upward trend among those ages 16 to 39 from FY2011 to FY2021 but showed a slight downward in FY2022. The same percentage increased slightly among those ages 40 to 64 from FY2014 to FY2020 but decreased slightly thereafter. For those ages 65 and older, a slight decrease has been observed from FY2011 to FY2022.
* Calculated based on height and weight measurements, with obesity defined as 25.0 or higher.
BMI= weight(kg) / height(m) / height(m)
Urinary Glucose, Urinary Protein, Urinary Occult Blood
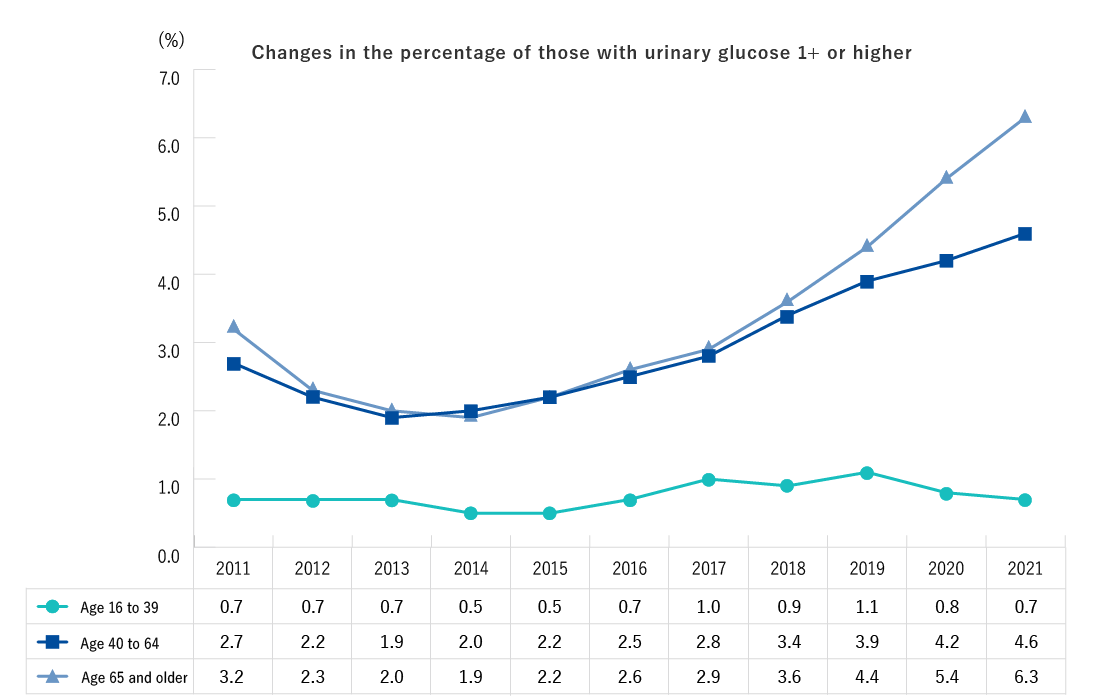
- The percentage with urinary glucose levels of 1+ or higher has seen an increasing trend since FY2015 in the age group of 40 years and older.
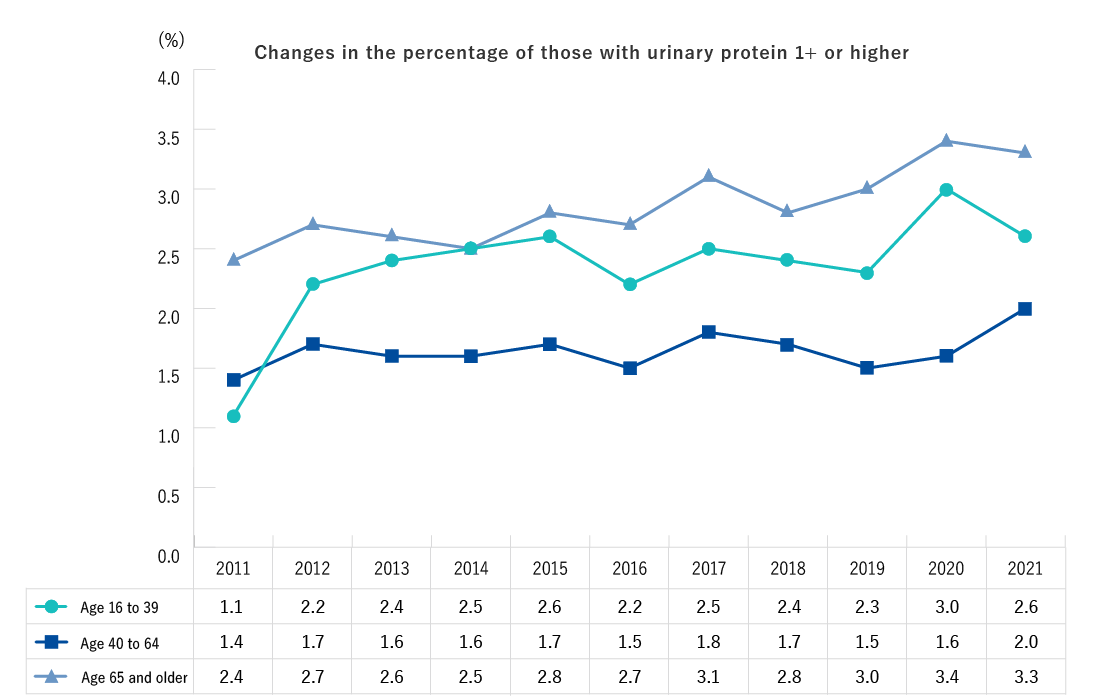
- The percentage of those with a urine protein level of 1+ or over increased among those ages 16 to 39 and those ages 65 or older from FY2011 to FY2020, but decreased thereafter.
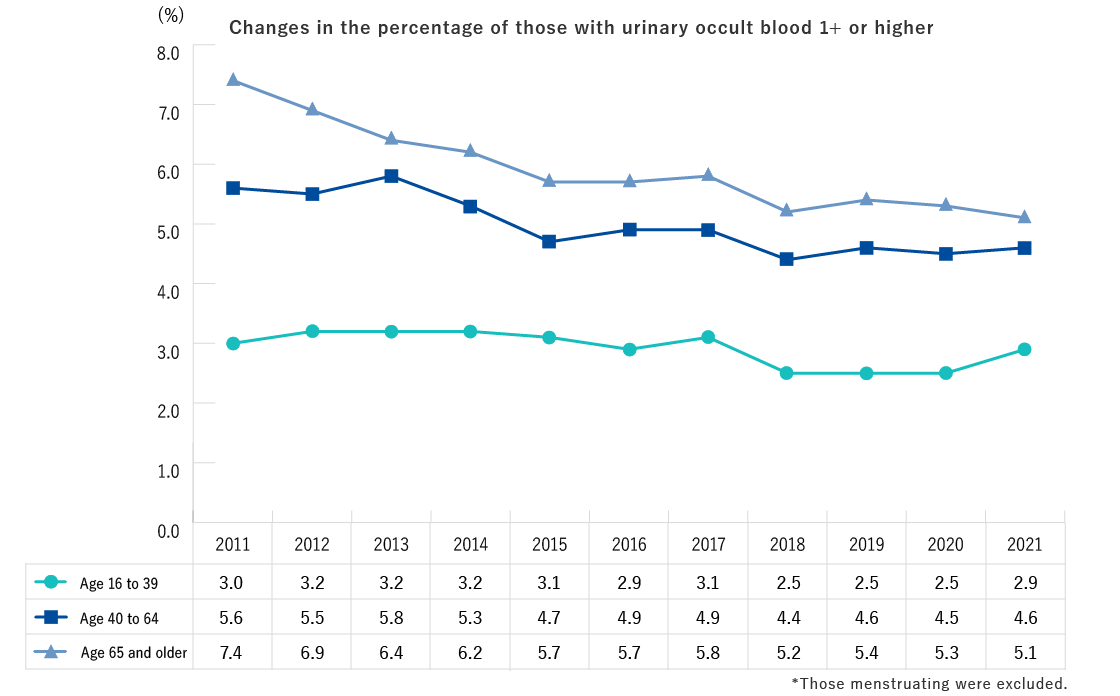
- The percentage with urinary occult blood levels of 1+ or higher showed a decreasing trend from FY2011 to FY2022 among those ages 65 and older.
* Abnormality of urine tests are determined based on the criteria used group health checks or individual health checks.
Diabetes
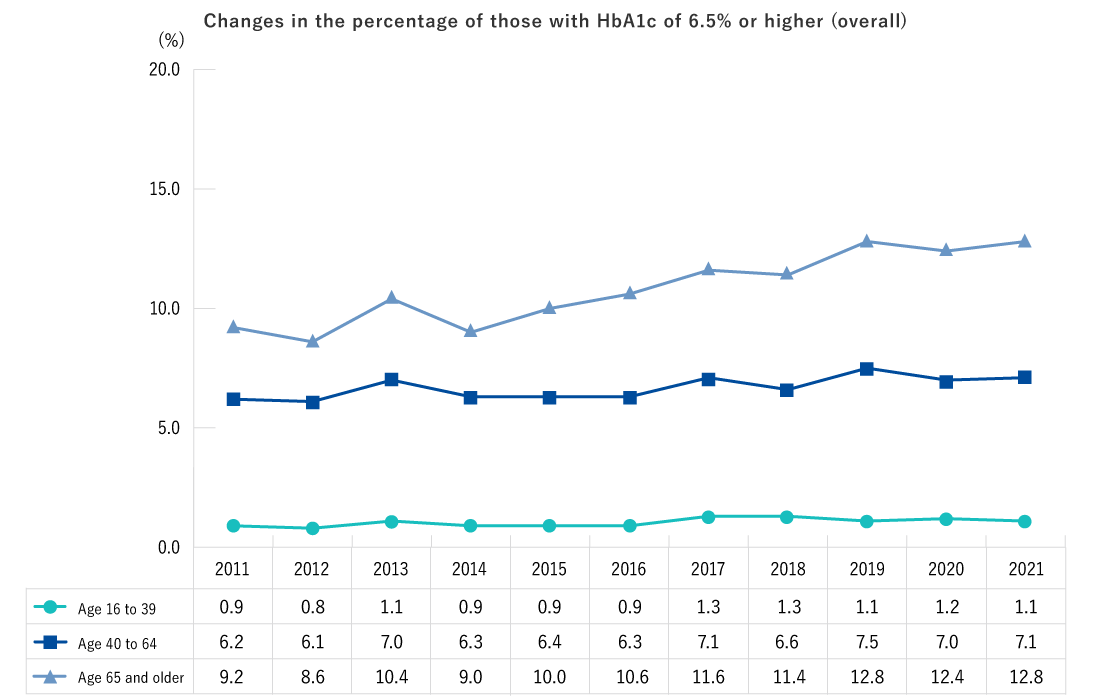
- The percentage with diabetes (HbA1c 6.5% or higher) showed an increasing trend from FY2011 to FY2022 among those ages 65 and older.
* Criteria are based on Clinical Practice Guideline for Diabetes of the Japan Diabetes Society
Uric acid
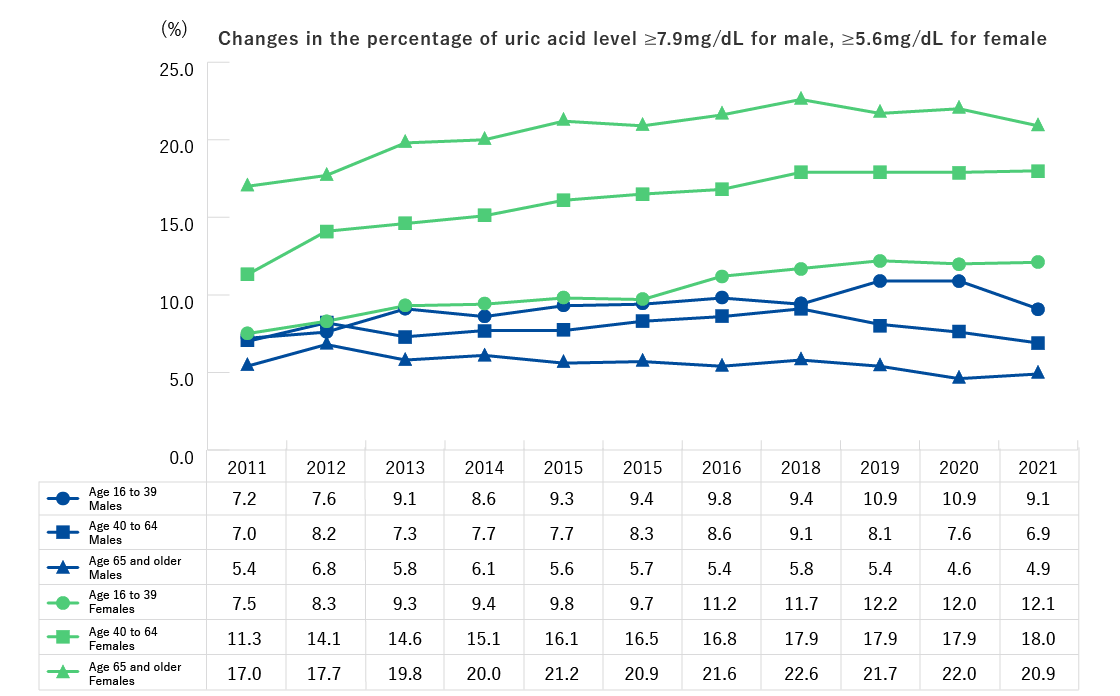
- The percentage of participants with uric acid of 7.9 mg/dL or over increased for males ages 16 to 39, it showed an increasing trend from FY2011 through FY2020 and showed a slight downward trend through FY2021, but there’s a slight increase percentage for and ages 40 to 64 showed a slight increase in FY2022.
- The percentage of females with uric acid of 5.6 mg/dL or over increased from FY2011 to FY2022 for those ages 40 to 64.
* Criteria are based on the Japanese Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards (JCCLS) Certified Reference Standard.
Summary
By ascertaining health conditions of the residents of evacuation areas, etc. through the Comprehensive Health Check, it was found that reduced physical activity and changes in diet due to evacuation may have affected the increases in residents’ obesity and overweight, and some diseases for which life as evacuees constitutes a risk factor were identified.
Residents ages 15 and younger
- The health check revealed the existence of a certain number of children who came to have obesity, hyperlipidemia, hyperuricemia, hepatic dysfunction, hypertension, and impaired glucose tolerance after the earthquake disaster.
- Subsequent follow-up surveys show an improvement in those children’s obesity but an improvement of hyperlipidemia has been delayed.
Residents ages 16 and older
- The analysis of WBC counts and DLCs of examinees within one year after the earthquake disaster revealed no direct impact of radiation.
- After the disaster, increases were observed in the incidence of obesity, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, diabetes, renal dysfunction, hepatic dysfunction, hyperuricemia, and polycythemia, and this suggests the possibility of an indirect impact of radiation (impact on health due to changes in living environment caused by evacuation, etc.). On the other hand, the percentage of those receiving treatment increased and examinees’ blood pressure values and LDL cholesterol counts showed signs of improvements. Additionally, an improvement of hepatic dysfunction was confirmed in association with better physical activity and diet.
- The analysis of changes in living environment, psychological indices, and health check items showed the association between posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and metabolic syndrome.
Outline of the Comprehensive Health Check
Purpose
The Great East Japan Earthquake and the accident at TEPCO’s Fukushima Daiichi NPS led to a large-scale evacuation of residents. Many of the evacuees have since been concerned about their own health due primarily to significant changes in their lifestyle such as diet and exercise habits, in addition to the loss of opportunity to undergo necessary health check. The Comprehensive Health Check was launched for residents in evacuation areas, with the aim of ascertaining their health status and using such data for the prevention of lifestyle diseases and early detection and treatment of diseases.
Eligible persons
- Those who were registered as residents in the covered area* from March 11, 2011 to April 1, 2012 (even after moving out of the area)
- Those who are registered as residents in the officially designated evacuation zone as of April 1 of each year of the CHC
- Other than those above, as necessary, based on Basic Survey results.
* Covered area: 13 municipalities designated by the national government as evacuation zones in 2011
Hirono Town, Naraha Town, Tomioka Town, Kawauchi Village, Okuma Town, Futaba Town, Namie Town, Katsurao Village, Iitate Village, Minamisoma City, Tamura City, Kawamata Town, and parts of Date City (specific spots recommended for evacuation)
Health check items by age group
| Age group | Health check items |
|---|---|
| Ages 0-6 (preschool children and infants) | Height, weight [The items below are performed upon request] CBC (number of red blood cells, hematocrit, hemoglobin, platelet count, number of white blood cells, differential white blood count) |
| Ages 7-15 (1st to 9th grade) | Height, weight, blood pressure, CBC (number of red blood cells, hematocrit, hemoglobin, platelet count, number of white blood cells, differential white blood count) [The items below are performed upon request] Blood biochemistry (AST, ALT, γ-GT, TG, HDL-C, LDL-C, HbA1c, plasma glucose, serum creatinine, uric acid) |
| Ages 16 and older | Height, weight, abdominal circumference (BMI), blood pressure, CBC (Number of red blood cells, hematocrit, hemoglobin, platelet count, number of white blood cells, differential white blood count), Urine test (urine sugar, urine protein, urine occult blood), Blood biochemistry (AST, ALT, γ-GT, TG, HDL-C, LDL-C, HbA1c, plasma glucose, serum creatinine, estimated glomerular filtration rate [eGFR], uric acid) * The underlined values are not measured in specific health checks. |
Implementation method
| Age | Place of regidence | Implementation method |
|---|---|---|
| 15 and younger | In the prefecture | Pediatric health checks at designated health check facilities in the prefecture |
| Outside the prefecture | Pediatric health checks at designated health check facilities in outside the prefecture | |
| 16 and older | In the prefecture |
|
| Outside the prefecture |
|



