Comprehensive Health Check
Outline of the Comprehensive Health Check
Purpose
The Great East Japan Earthquake and the accident at TEPCO’s Fukushima Daiichi NPS led to a large-scale evacuation of residents. Many of the evacuees have since been concerned about their own health due primarily to significant changes in their lifestyle such as diet and exercise habits, in addition to the loss of opportunity to undergo necessary health check. The Comprehensive Health Check was launched for residents in evacuation areas, with the aim of ascertaining their health status and using such data for the prevention of lifestyle diseases and early detection and treatment of diseases.
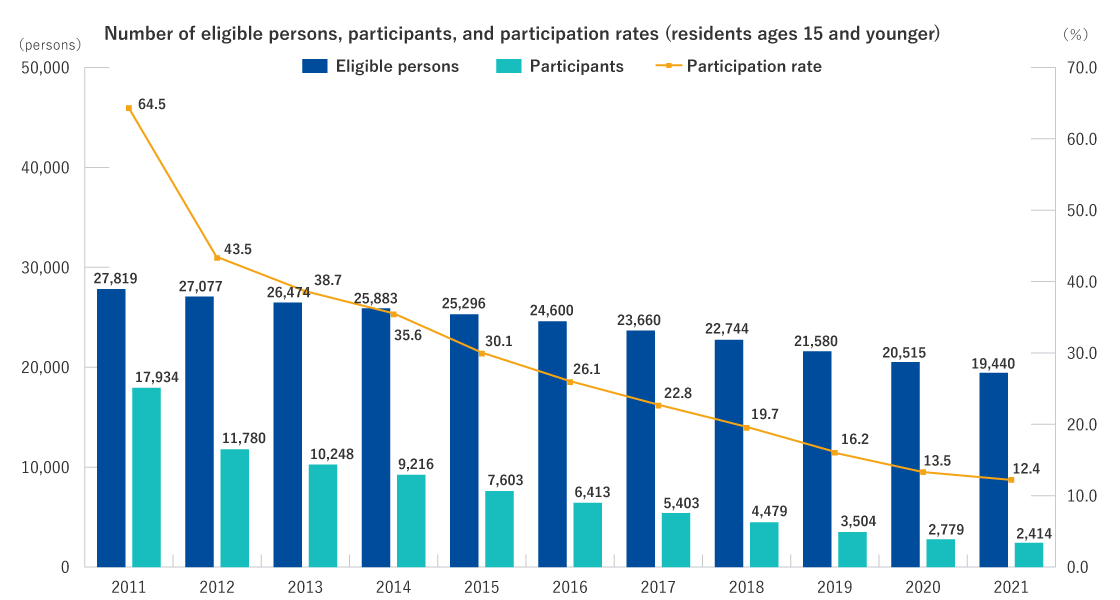
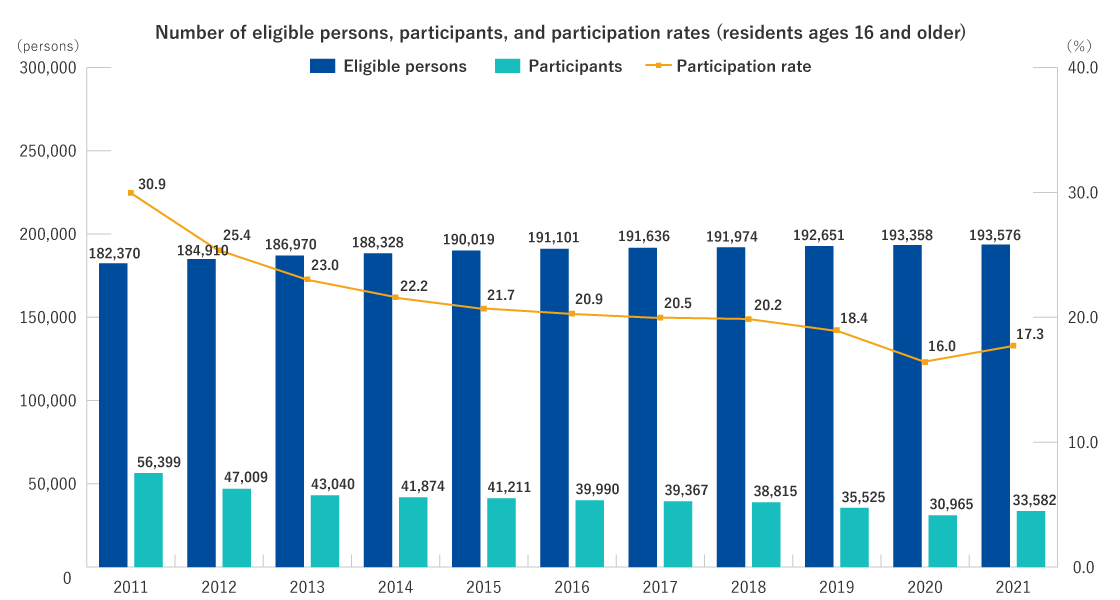
Eligible persons
- Those who were registered as residents in the covered area* from March 11, 2011 to April 1, 2012 (even after moving out of the area)
- Those who are registered as residents in the officially designated evacuation zone as of April 1 of each year of the CHC
- Other than those above, as necessary, based on Basic Survey results.
* Covered area: 13 municipalities designated by the national government as evacuation zones in 2011
Hirono Town, Naraha Town, Tomioka Town, Kawauchi Village, Okuma Town, Futaba Town, Namie Town, Katsurao Village, Iitate Village, Minamisoma City, Tamura City, Kawamata Town, and parts of Date City (specific spots recommended for evacuation)
Health check items by age group
| Age group | Health check items |
|---|---|
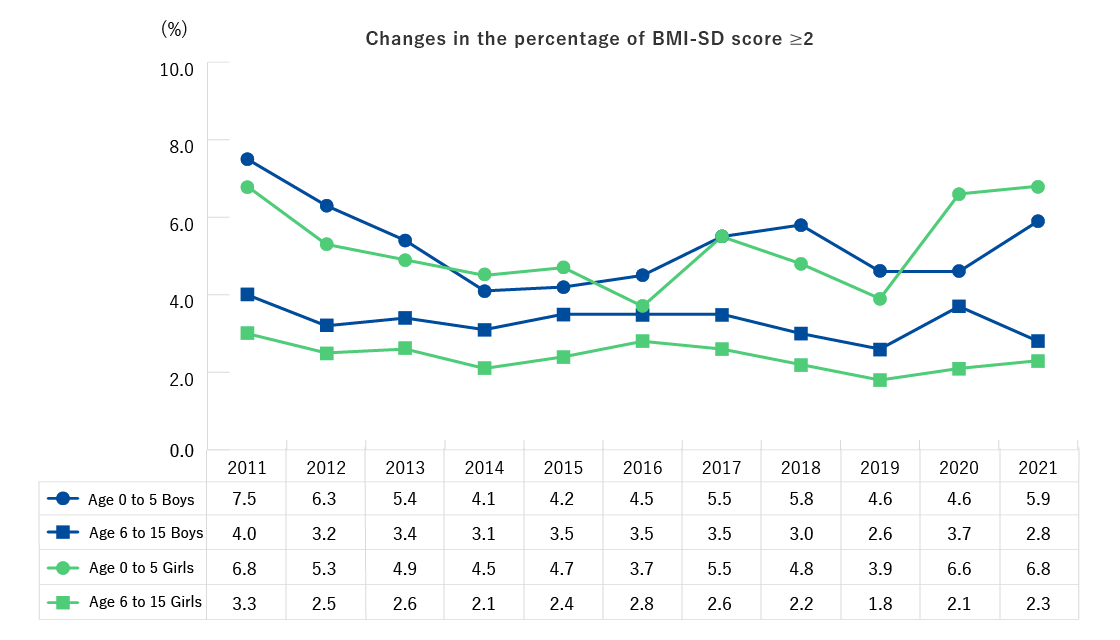
| Ages 0-6 (preschool children and infants) | Height, weight [The items below are performed upon request] CBC (number of red blood cells, hematocrit, hemoglobin, platelet count, number of white blood cells, differential white blood count) |
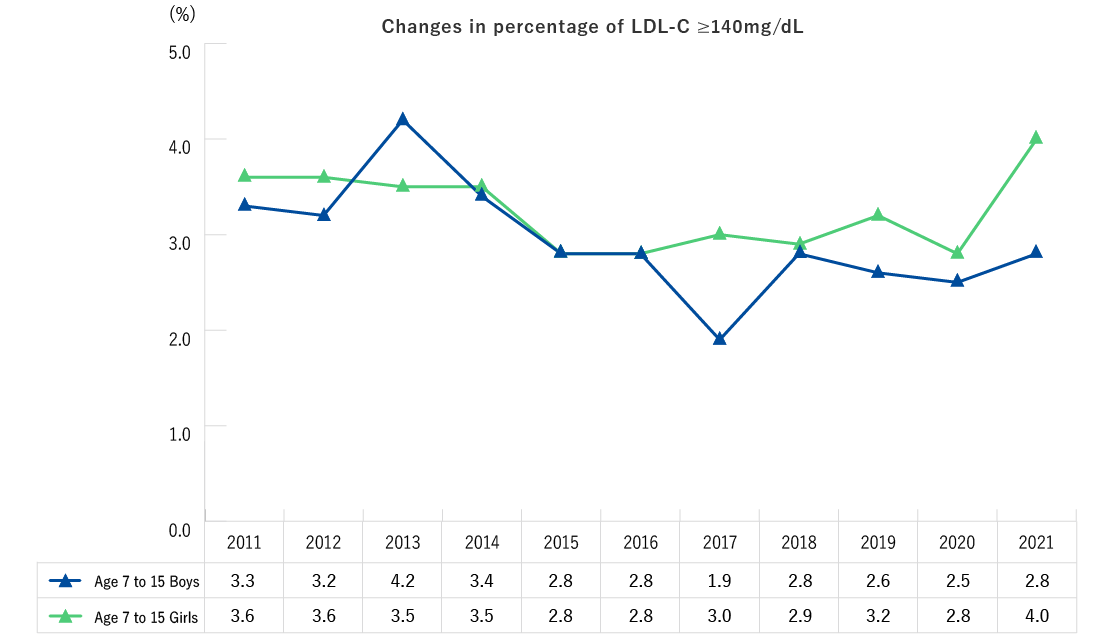
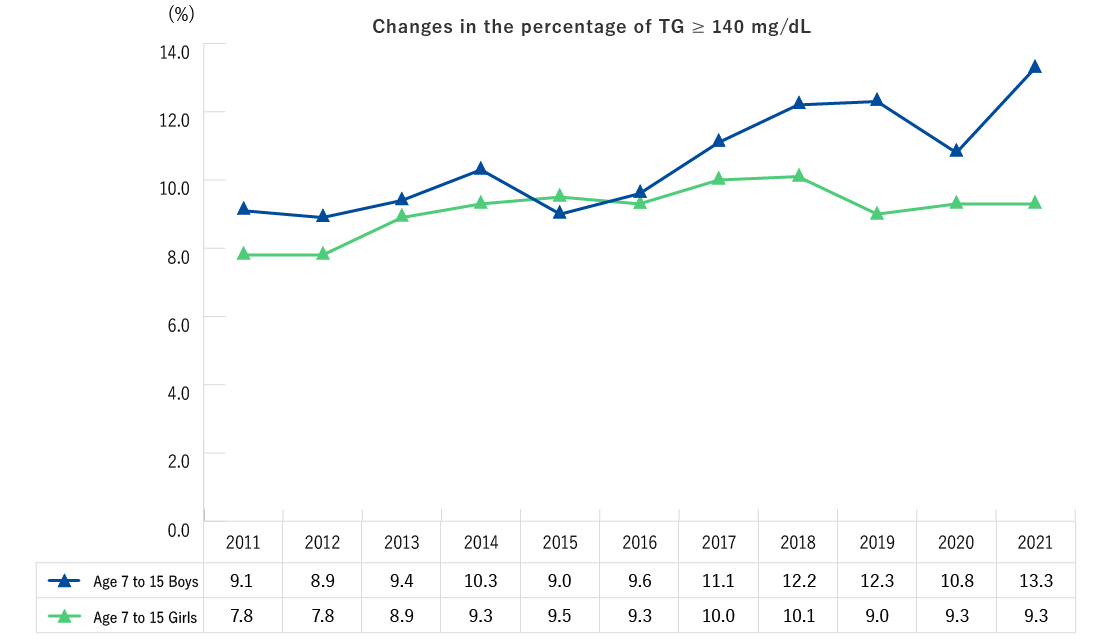
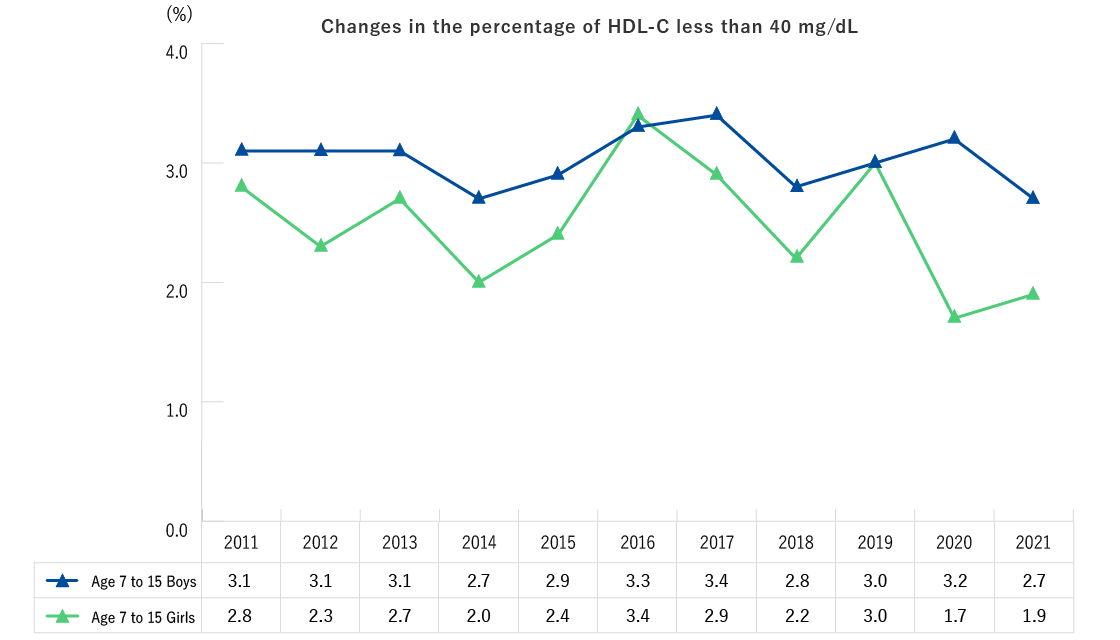
| Ages 7-15 (1st to 9th grade) | Height, weight, blood pressure, CBC (number of red blood cells, hematocrit, hemoglobin, platelet count, number of white blood cells, differential white blood count) [The items below are performed upon request] Blood biochemistry (AST, ALT, γ-GT, TG, HDL-C, LDL-C, HbA1c, plasma glucose, serum creatinine, uric acid) |
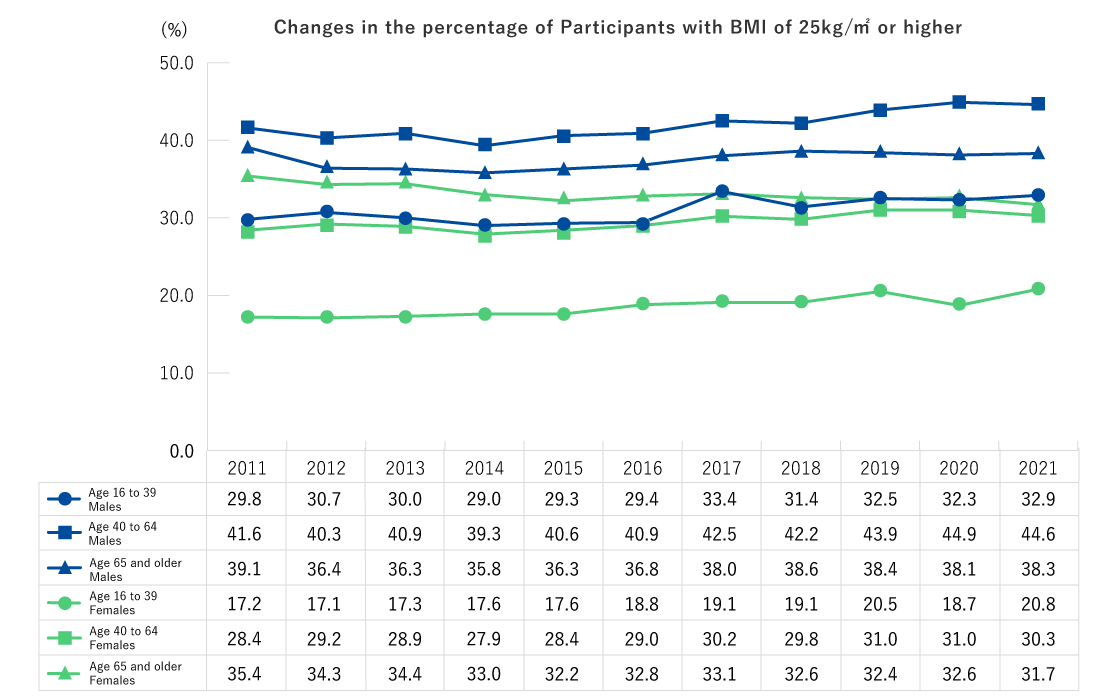
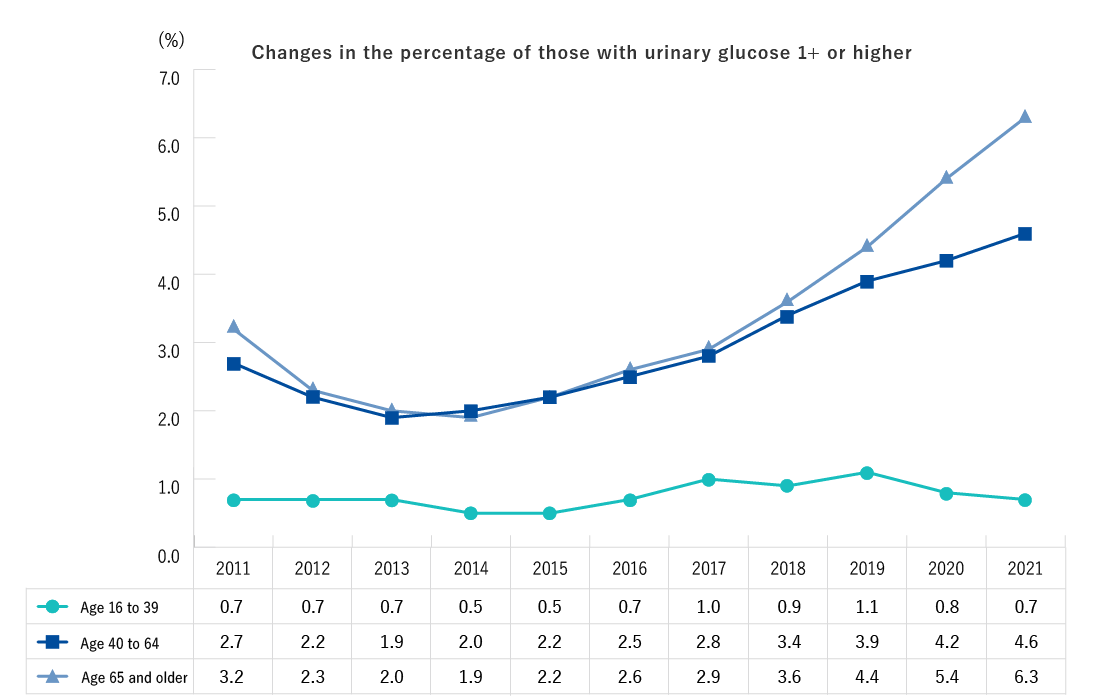
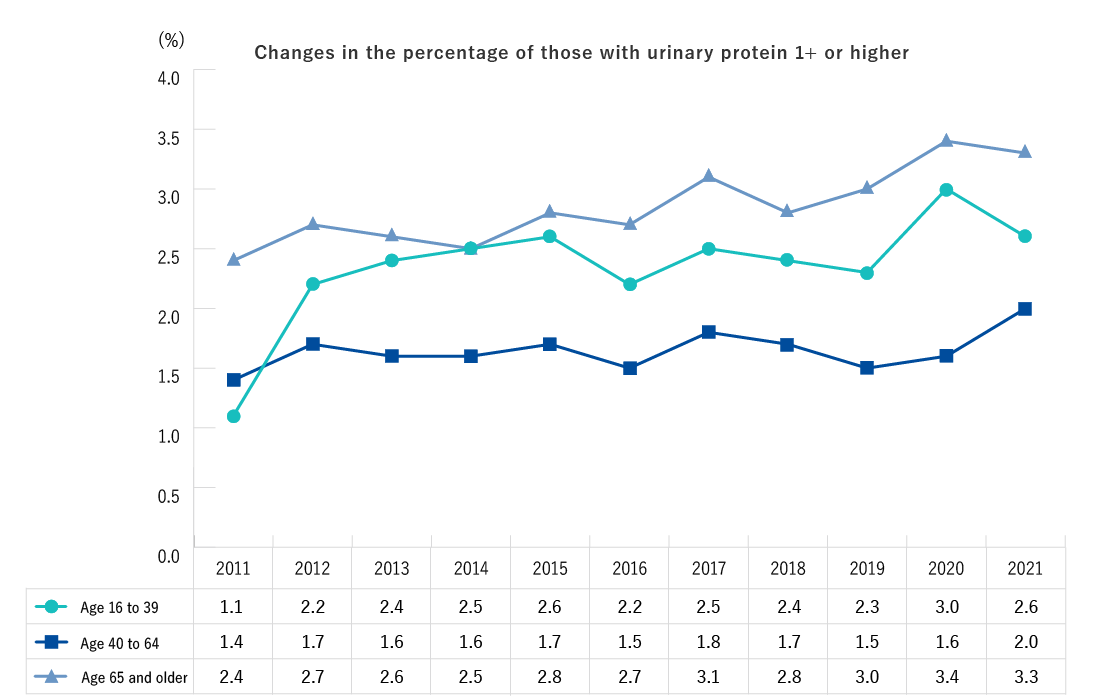
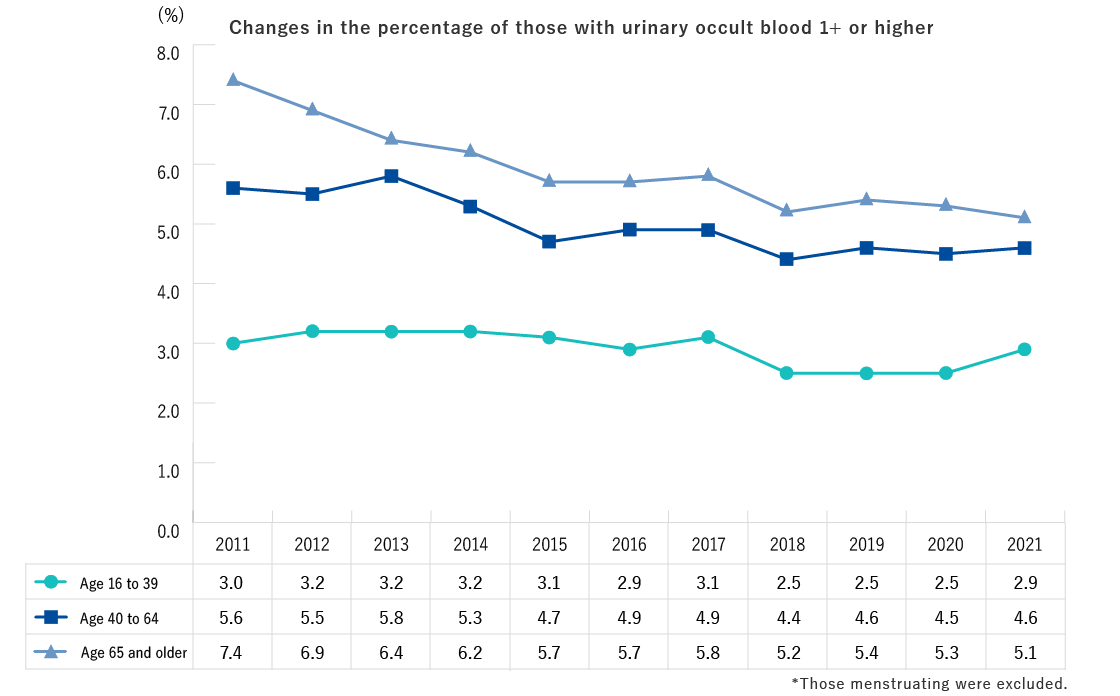
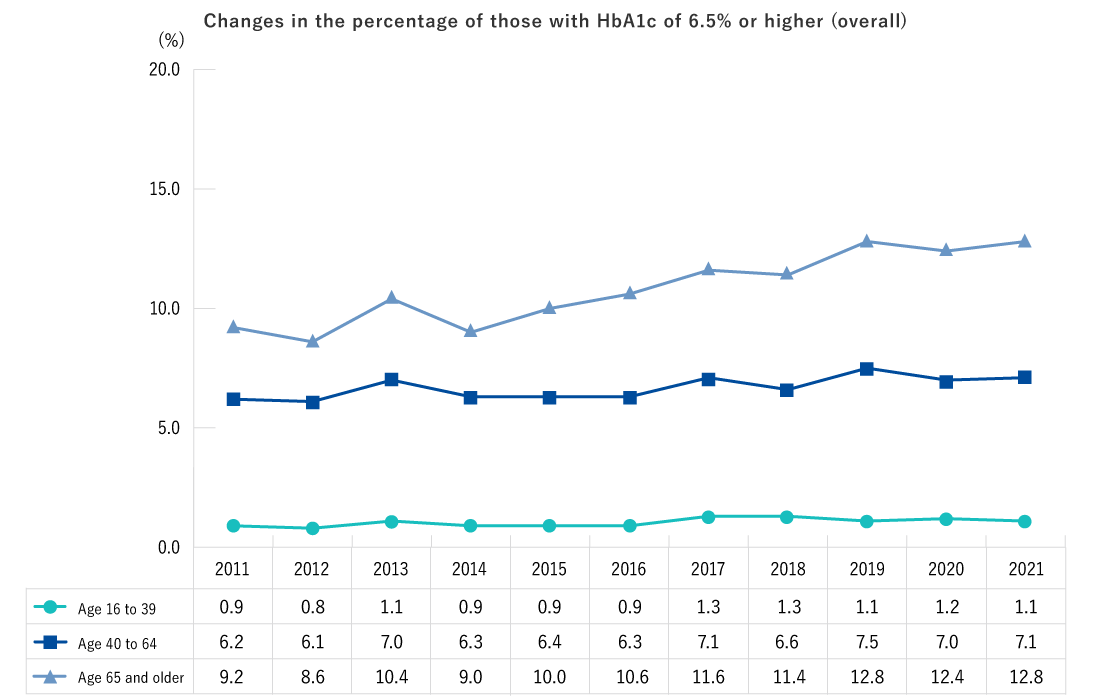
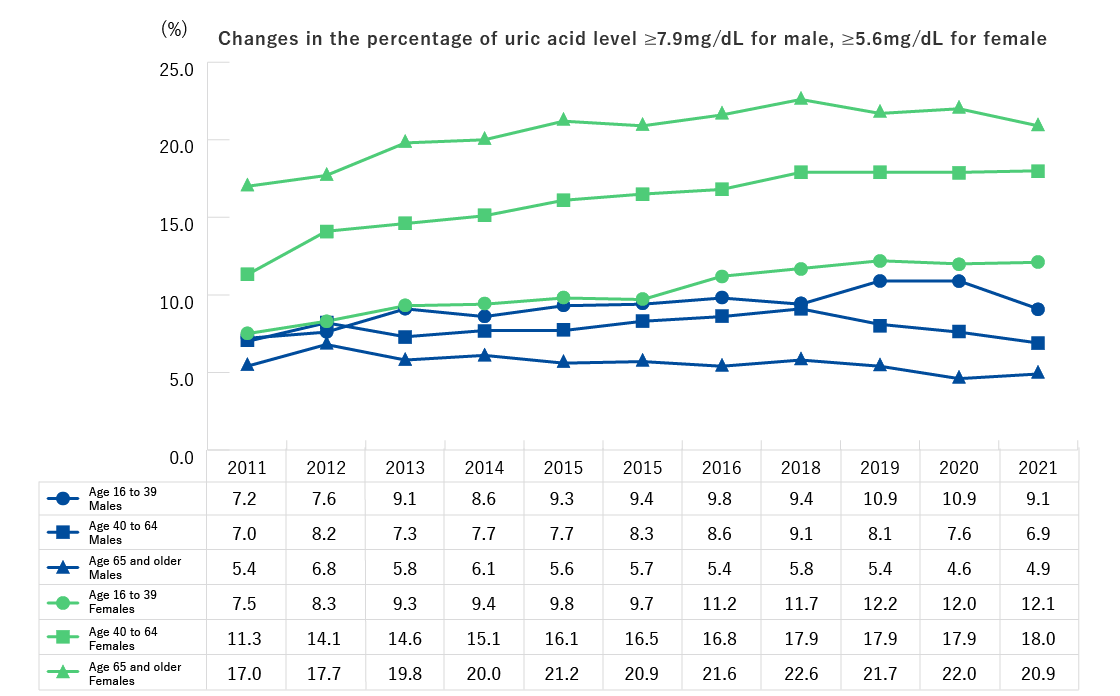
| Ages 16 and older | Height, weight, abdominal circumference (BMI), blood pressure, CBC (Number of red blood cells, hematocrit, hemoglobin, platelet count, number of white blood cells, differential white blood count), Urine test (urine sugar, urine protein, urine occult blood), Blood biochemistry (AST, ALT, γ-GT, TG, HDL-C, LDL-C, HbA1c, plasma glucose, serum creatinine, estimated glomerular filtration rate [eGFR], uric acid) * The underlined values are not measured in specific health checks. |
Implementation method
| Age | Place of regidence | Implementation method |
|---|---|---|
| 15 and younger | In the prefecture | Pediatric health checks at designated health check facilities in the prefecture |
| Outside the prefecture | Pediatric health checks at designated health check facilities in outside the prefecture | |
| 16 and older | In the prefecture |
|
| Outside the prefecture |
|